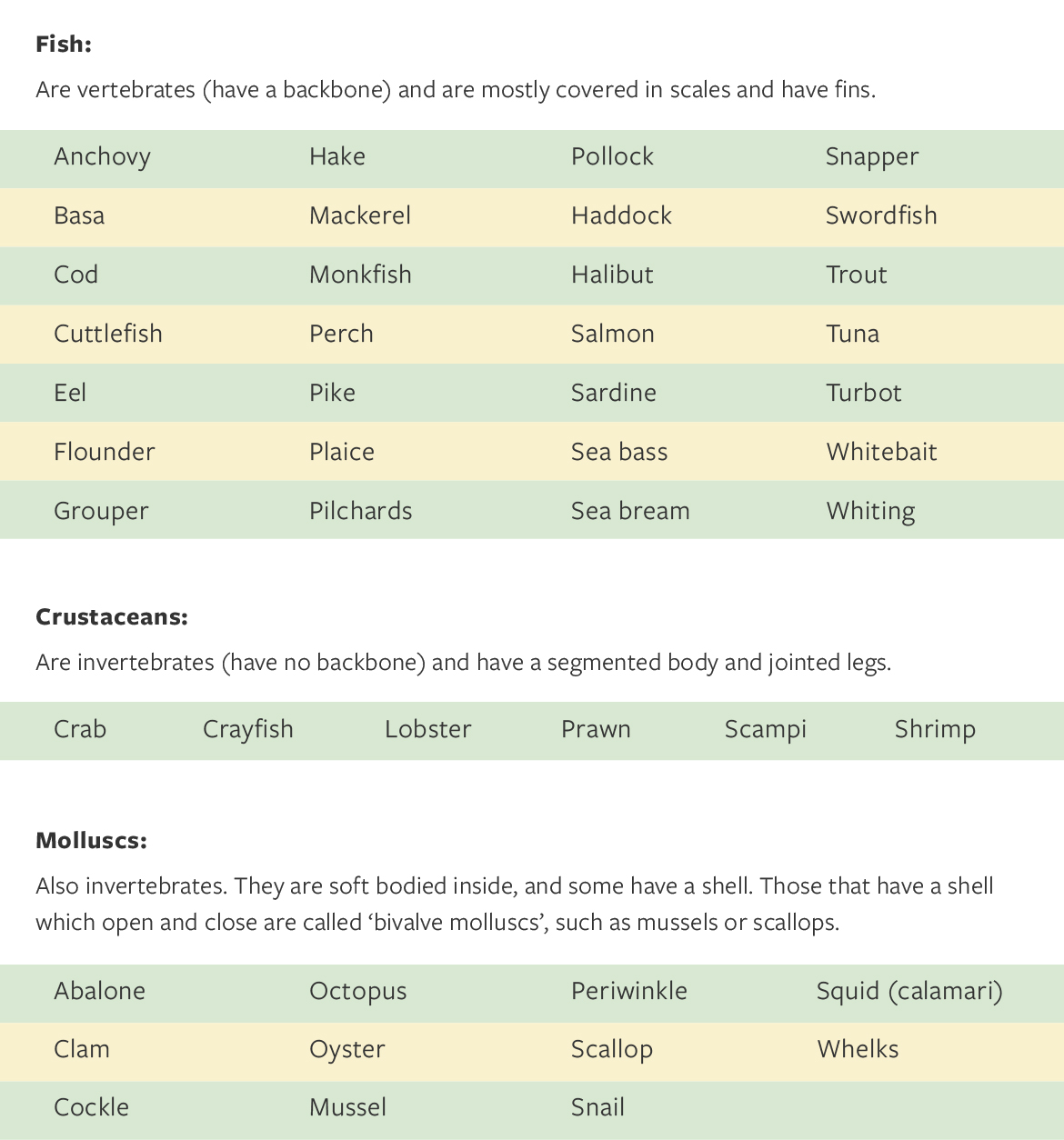
Fish and Seafood (molluscs and crustaceans)
Seafood is a staple of many countries and a delicacy in many more. It`s not surprising then, that the total amount of seafood consumed worldwide is on the rise.
However, seafood allergies are one of the most common food allergies in adults, and can also affect children. Seafood allergies can develop at any point in a person`s life and can even be caused by a fish or shellfish that has been eaten before with no previous signs of an allergy; once the allergy is discovered, it`s likely to be lifelong and rarely outgrown.
Fish and Shellfish:
Seafood is used as a collective term that includes both fish and shellfish. However, shellfish is further divided into crustaceans or molluscs. See the tables below for more information.
Fish and Shellfish in the Diet:
Whilst some forms of fish or shellfish may be visible in food, other forms may be hidden, or not obvious by sight or smell. The following list of foods are common culprits for containing fish and shellfish in different dishes:
- Asian foods may contain fish or shellfish mixed with other foods (such as prawn fried rice) or fish and shellfish disguised in stocks or sauces
- Rice dishes such as paella, fried rice and sushi rolls may contain fish or shellfish
- Fish and shellfish can be disguised in a batter or crumb coating such as scampi, fish fingers or seafood sticks
- Stews, soups or casseroles such as seafood chowder or bouillabaisse
- Dips or pates containing fish such as taramasalata, salmon and caviar or roe (fish eggs)
- Anchovy (fish) may be in Caesar salads, added as a pizza topping or in a sauce
- Sauces that contain fish, including Worcestershire, oyster and fish sauces which can be added to many different types of dishes, including casseroles and stir fries
- Pizza toppings such as prawn, anchovy, calamari, mussels and fish
- Foods cooked in the same batter or oil (for example fish and chips from a takeaway shop).
This list isn`t exhaustive and the key is to read labels carefully and make sure you ask questions about the ingredients in prepared foods when eating away from home. If you are allergic to one type of shellfish or fish, it`s generally safer to avoid all types when eating out, due to the risk of cross contamination.
If eating overseas, for example on holiday, be aware that different countries have different words for fish and shellfish. For example, lobster may be called langoustine, or squid may be labelled as calamari.
Cross contamination occurs when one food type comes into contact with another food and their proteins (the allergy causing substance) mix. For people who are highly sensitive to small amounts of these proteins, they may develop allergic symptoms from eating, inhaling or handling fish and shellfish.
Fish and prawn allergens can be very robust and not easily broken down by heating or cooking, they can even become airborne in cooking vapours or present in oil used to cook fish or prawns. Because of this, cross contact has the potential to happen in any area where food is handled, like in the home, food processing factories, or a catering outlets.
Cross Contact can either be direct, where the allergen was included in a food and then removed (e.g. nuts removed from the top of a cake), or indirect, which happens when a food allergen is not directly applied (e.g. when the same scoop is used to serve a vanilla ice cream and an ice cream containing nuts).
Complementary Supplements may contain Fish or Shellfish:
Glucosamine is a natural chemical compound in your body that also comes in the form of a supplement, which is linked to joint health and can be taken by those with arthritis. It is derived from the outer coating of a shellfish and can sometimes also contain "˜chondroitin`, which is derived from shark cartilage.
Many people also take fish oil supplements for general health benefits, and while these go through an extensive process to remove impurities, it can`t be guaranteed that all allergens have been removed. It`s advisable therefore, for people with a fish or shellfish allergy to avoid these supplements, as they may still contain small amounts of fish proteins.
Fish and Shellfish Allergic Symptoms:
An allergic reaction to seafood can be mild or moderate (swollen lips, face or eyes, itching, tingling mouth, hives, rash, abdominal pain, vomiting) or severe (breathing difficulties, dizziness or collapse), and it has the potential to cause anaphylaxis (the most severe form of an allergic reaction).
People with allergies may experience one or more of the following:
Mild to moderate symptoms:
- Hives (rash)
- Tingling mouth
- Swelling of the lips, face, tongue or throat
- Itching
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Abdominal pain
- Diarrhoea
Severe symptoms:
- Difficult or noisy breathing
- Wheezing
- Persistent cough
- Chest tightness
- Hoarse voice
- Difficulty swallowing